
#Mount mac nfs share windows 10 keygen

This USRPRF then becomes a group profile and can be assigned to all of the users that participate in this NFS operation through the Group profile parameter or through the supplemental groups parameter: To apply a GID to a USRPRF, a user profile must be created with a number in the GID parameter. If a group of people needs to have access to this file structure, a GID is recommended. GID and UID are used in a similar fashion. For example, if the users require RWX, that is required for *PUBLIC on both ends of the connection. The public authority given to the directory structure depends on what type of operations must be performed on these files. The easiest and least secure method is to use *PUBLIC authority. The QNFSANON user ID is used when a client passes a UID/GID that is unknown to our server. NFS uses UIDs and GIDs for all file permissions rather than a user ID and password. QNFSNSMD (Network Status Monitor Daemon) monitors the status of all clients connected and notifies all interested parties when the state of a client changes. QNFSNLMD (Network Lock Manager Daemon) locks a file system while it is in use. If they are allowed to mount, it sends back a file handle that uniquely describes the file structure. This job checks to see if the client is allowed to mount over the file system they are requesting. QNFSMNTD (Mount Daemon) listens for client requests involving mounting. There are four other jobs that are used in both roles: QNFSRPCD (RPC Binder Daemon) is the port mapper job and determines the port of a specified RPC service in this case, NFS. There can be multiple instances of both of these jobs to handle data transfers in parallel. It handles all of the data transactions from the clients. The QNFSNFSD is the server side job on the iSeries. The QNFSBIOD (Block I/O Daemon) handles caching and routing to the server when the iSeries is the client. The client then mounts over this exported file system. The server in NFS is the system that is doing the EXPORT. NFS normally uses the UDP protocol (at R610 and above it can also use TCP) and servers listen on port 2049. Traffic between the client and server uses the remote procedure call mechanism described in RFC 1057. Data values are encoded using a method known as XDR (external data representation) described in RFC 1014.
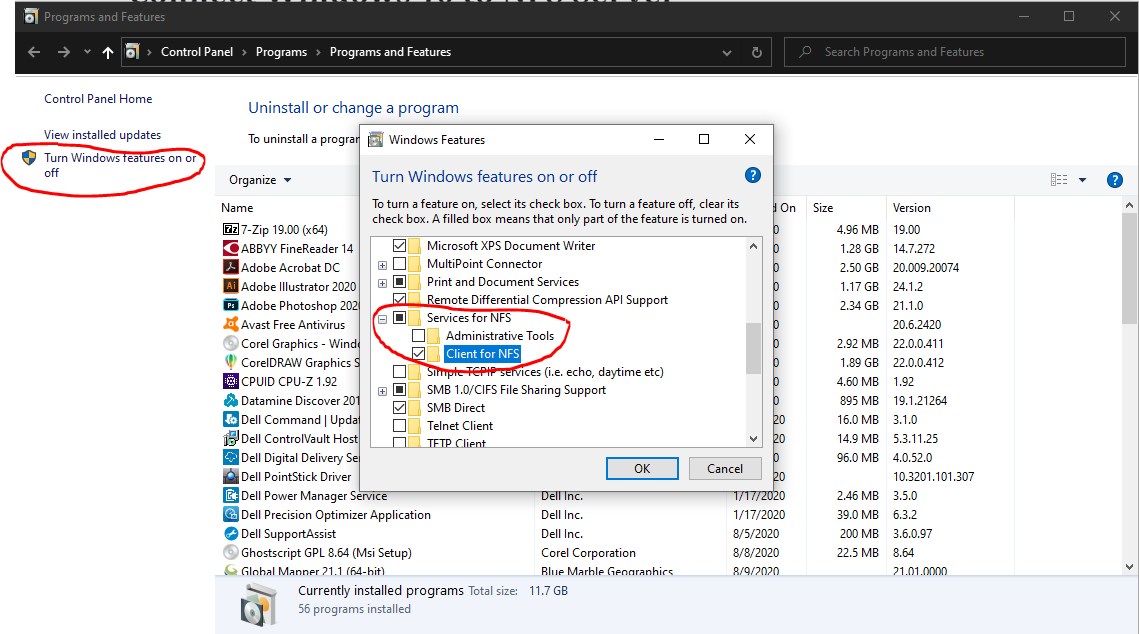
The networked file system operates on a client-server basis using network messages to transfer requests and data between clients and servers. Version 3 of the protocol defined in RFC 1813 was published in 1995. It has been widely implemented on other platforms.

It was first described by Sun Microsystems Inc in 1989 and has been part of their standard product offerings since that date. The networked file system (known as NFS and defined in RFC 1094) is used to allow hosts to share files across a network. This document will highlight the major areas of NFS, and should assist you in understanding and troubleshooting common NFS problems.


 0 kommentar(er)
0 kommentar(er)
